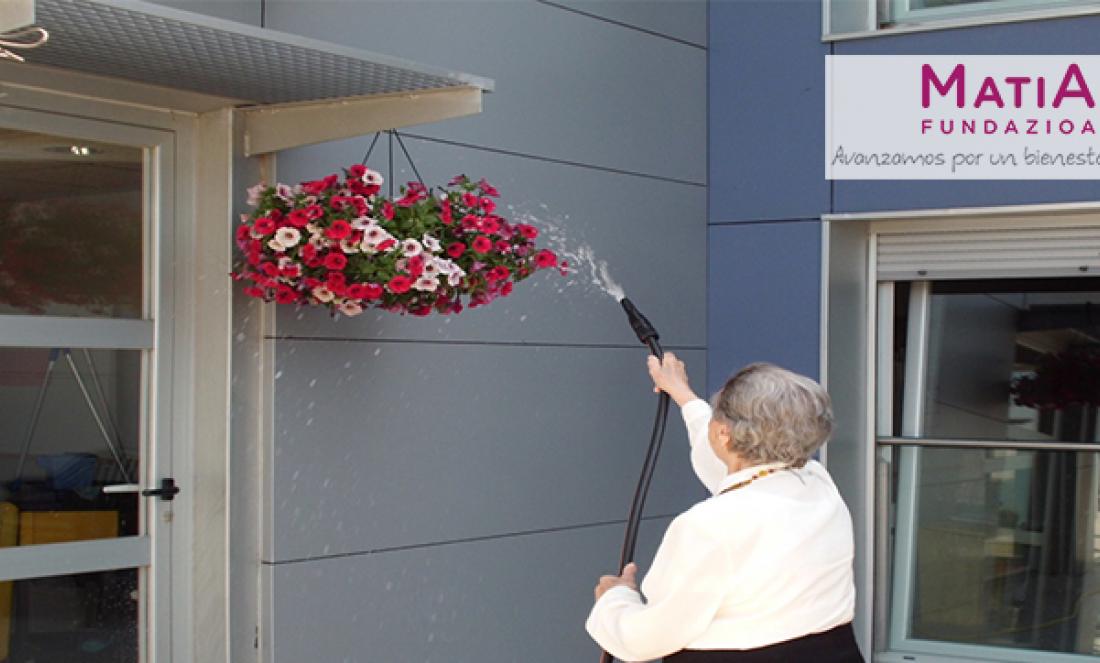

Design and implementation of outdoor activities
Objectives:
With the implementation of the person-centred care model and the commitment to contribute to the improvement of the quality of life of the residents, the importance of implementing outdoor activities became clear.
Based on the life history, the care team proposed to design and implement these activities that would respond to the expectations and desires of residents and families.

Method:
The project started in spring 2011:
- Revision of the life history, capturing hobbies and user expectations in relation to outdoor activities
- Identification and design of activities.
- Structuring and adaptation of the terrace.
- Assignment of users by activities.
- Setting up of the activities.
- Evaluation
Results:
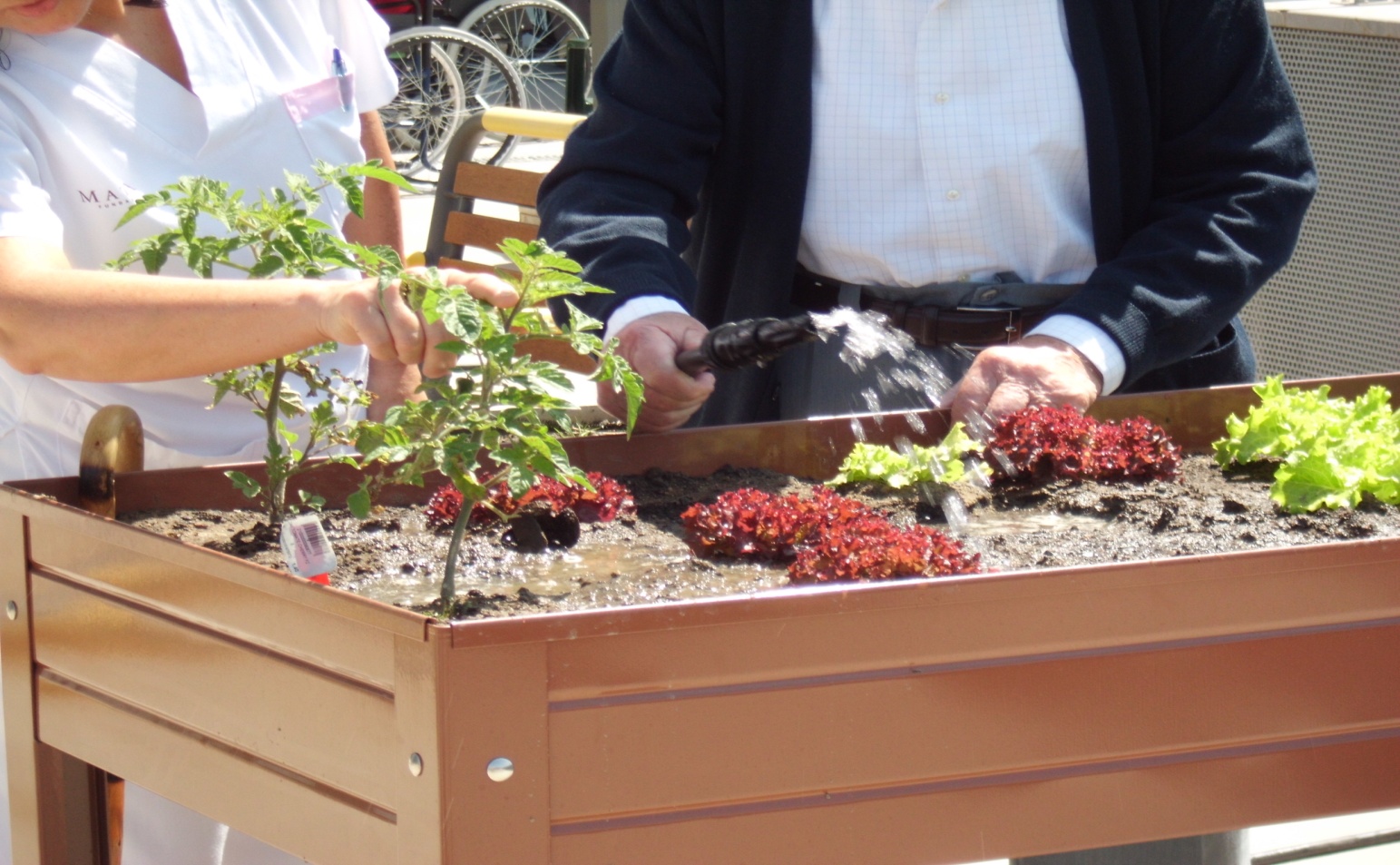
The activities initially identified were: horticulture and leisure activities. At the same time, the team identified cognitive stimulation activities and basal psychostimulation activities, mainly oriented to people with cognitive impairment
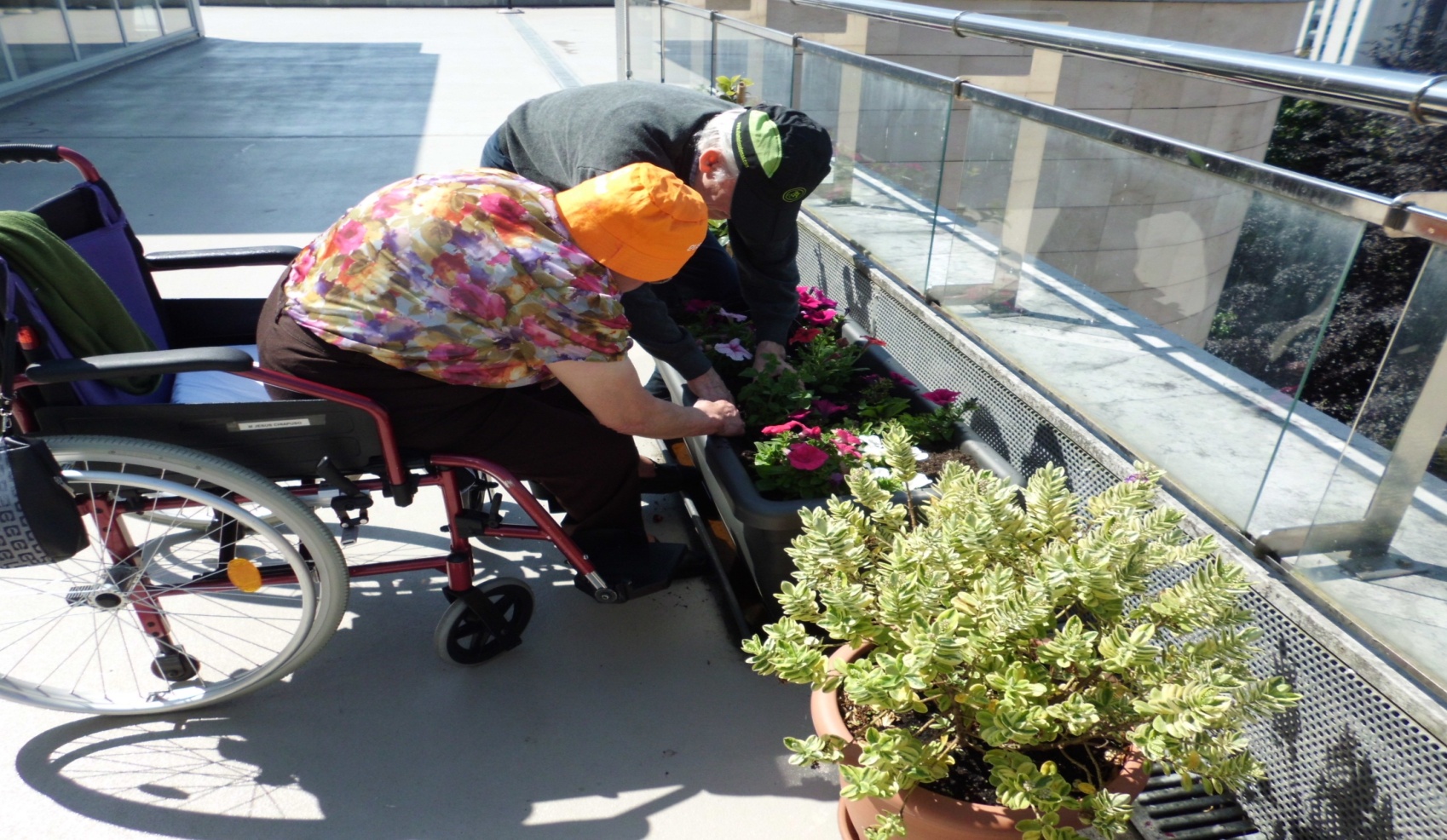

The collaborating company (GERODAN) designed the terrace and acquired the main elements for its structuring and sectorisation.
The plants and seedlings were purchased and planted with the participation of the previously selected residents. The "bring your flower" campaign began, which consisted of each family bringing a flower to be looked after by their relative...
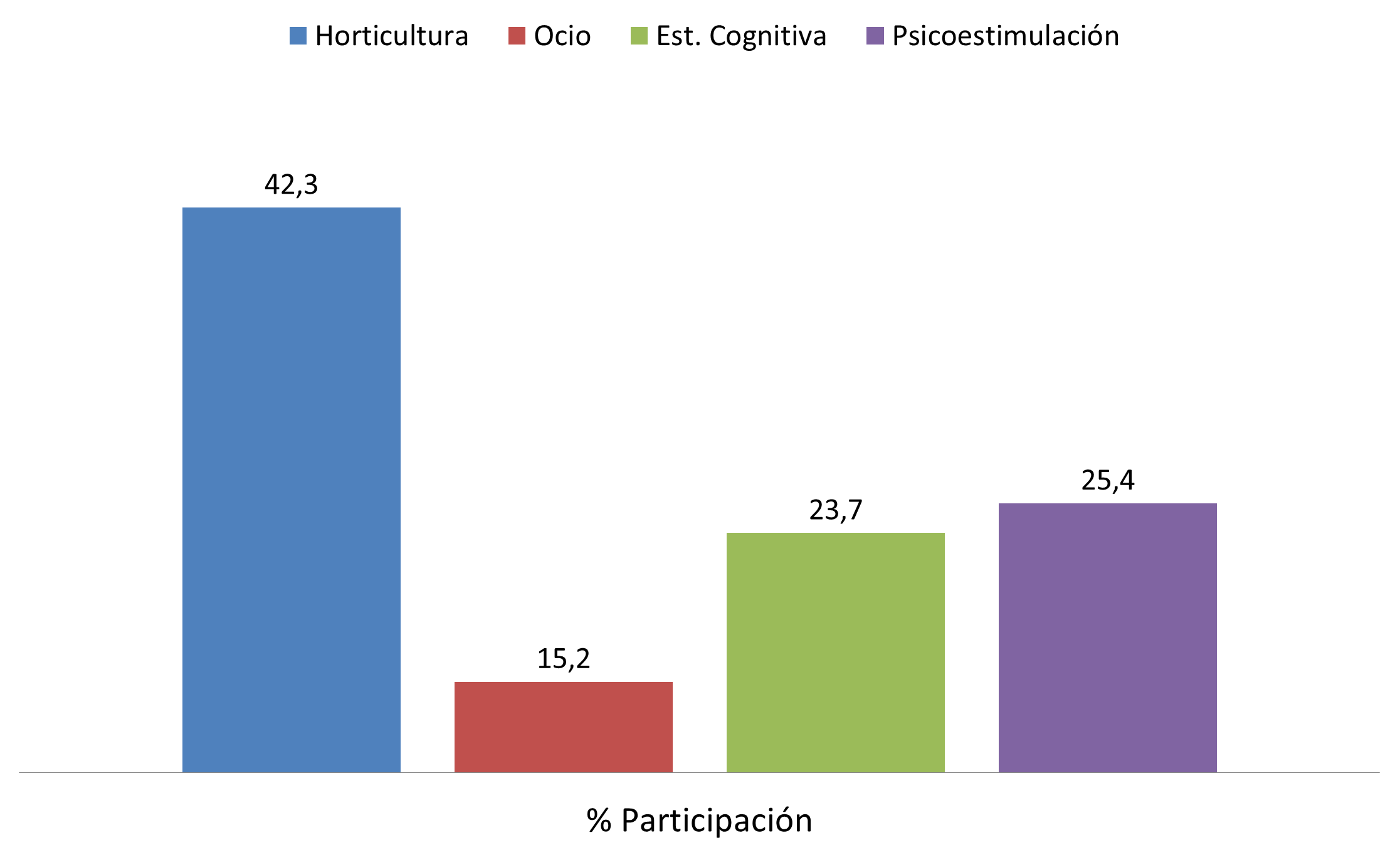
In total, 84.7% of the residents were involved and enjoyed the activities designed, which the team considered a success. Specifically:
- Horticulture: 42.3% of the residents work in the garden.
- Leisure and free time activities: 15.2% of residents use the terrace to be outdoors.
- Cognitive stimulation activities: 23.7% of residents use the terrace to carry out reality-based activities.
- Basal psychostimulation activities: 25.4% of residents use the terrace as a sensory space for psychostimulation.
Conclusions:
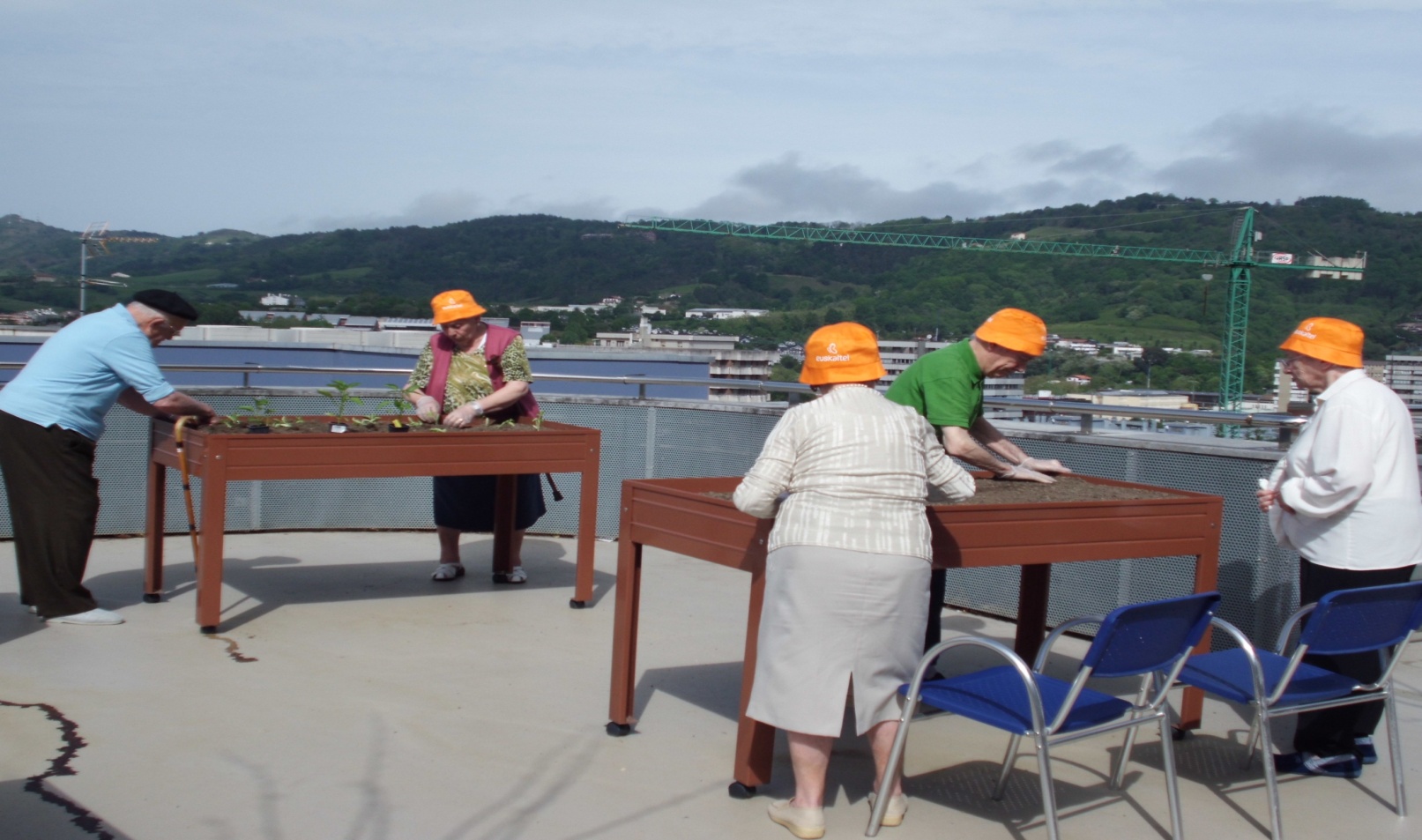

The large percentage of residents involved in the activities shows satisfaction with these programmes.

Add new comment